3 Ligaments Of The Hip. The capsule of the hip joint attaches to the edge of the acetabulum proximally. In vertebrate anatomy, hip (or coxa in medical terminology) refers to either an anatomical region or a joint. Distally, it attaches to the intertrochanteric line anteriorly and the femoral neck. The ligaments of the hip joint are as follows: The hip region is located lateral and anterior to the gluteal region, inferior to the iliac crest. Maintain lubrication in the joint by aiding the distribution of synovial fluid. Inclusive of ischiofemoral ligament, iliofemoral ligament and pubofemoral ligament. Additional hip stabilizer in patients with generalized ligamentous laxity, hip dysplasia and in patients with anteroinferior acetabular deficiency. This video identifies all ligaments of the hip. Aids fine coordination of the hip joint. The depth of the acetabulum and narrowing of its mouth by the acetabular labrum. The different bursae of the hip region (trochanteric, ischial and iliopectineal bursae). Dislocation of the hip joint. The firmness of the hip joint is supplied by the following factors which help prevent its dislocation: The main ligaments of the hip and its associated area (iliofemoral, ishciofemoral ligament and pubofemoral ligaments, ligament of bursae of the lower limb:
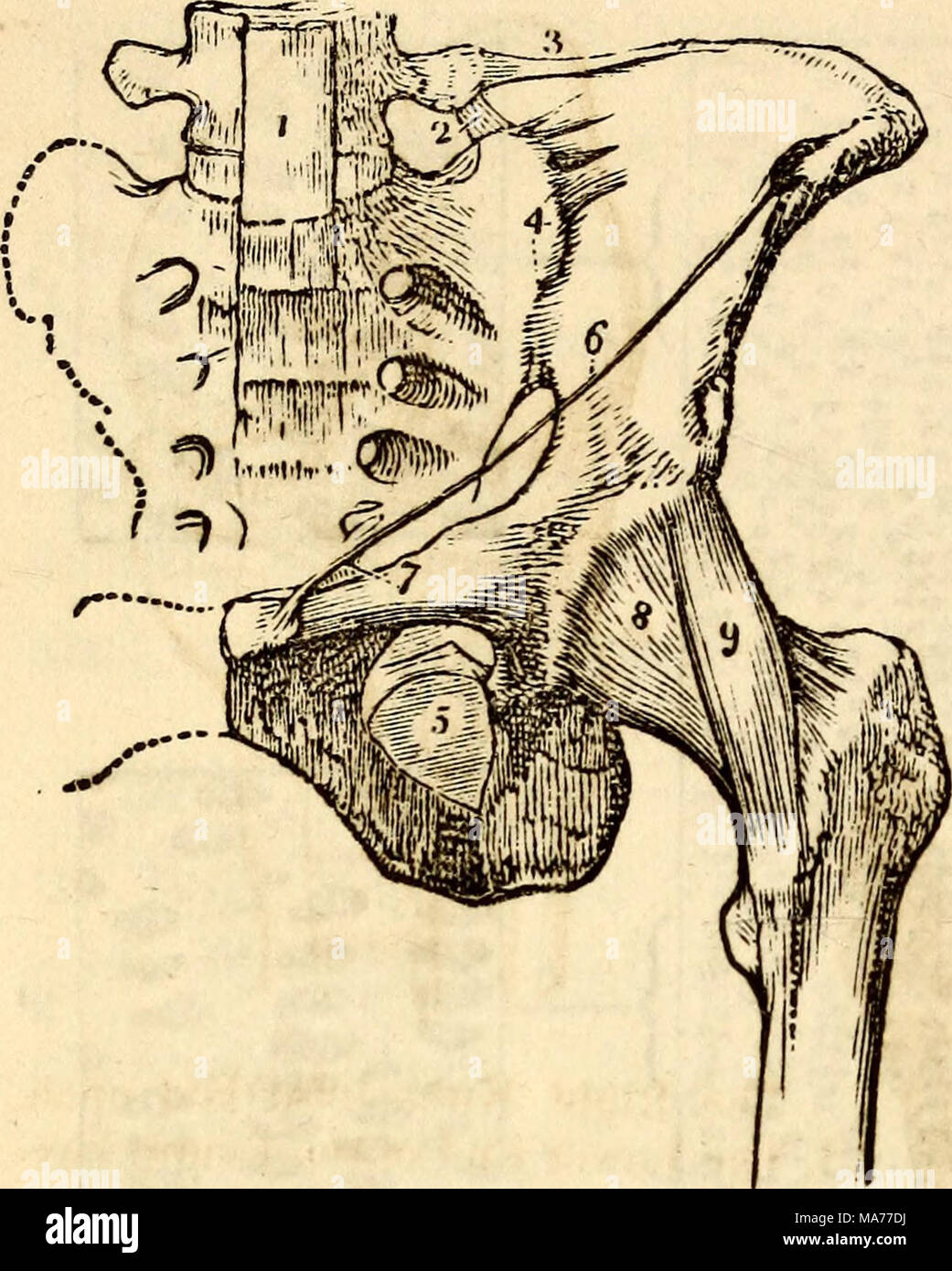
3 Ligaments Of The Hip - 6, Cotyloid Ligament Around The Acetabulum;
Hip Model 3 Gpi Anatomicals. Maintain lubrication in the joint by aiding the distribution of synovial fluid. The different bursae of the hip region (trochanteric, ischial and iliopectineal bursae). Distally, it attaches to the intertrochanteric line anteriorly and the femoral neck. Dislocation of the hip joint. In vertebrate anatomy, hip (or coxa in medical terminology) refers to either an anatomical region or a joint. The depth of the acetabulum and narrowing of its mouth by the acetabular labrum. The main ligaments of the hip and its associated area (iliofemoral, ishciofemoral ligament and pubofemoral ligaments, ligament of bursae of the lower limb: Inclusive of ischiofemoral ligament, iliofemoral ligament and pubofemoral ligament. Additional hip stabilizer in patients with generalized ligamentous laxity, hip dysplasia and in patients with anteroinferior acetabular deficiency. This video identifies all ligaments of the hip. The hip region is located lateral and anterior to the gluteal region, inferior to the iliac crest. The firmness of the hip joint is supplied by the following factors which help prevent its dislocation: The capsule of the hip joint attaches to the edge of the acetabulum proximally. The ligaments of the hip joint are as follows: Aids fine coordination of the hip joint.
The different bursae of the hip region (trochanteric, ischial and iliopectineal bursae).
The firmness of the hip joint is supplied by the following factors which help prevent its dislocation: Pcl reconstruction rehabilitation online course: In anatomy, a ligament is a band or sheet of strong fibrous connective tissue that connects bones to other bones, or to cartilage, or supports an organ, such as the spleen, uterus, or eyeball. The capsule of the hip joint attaches to the edge of the acetabulum proximally. 6, cotyloid ligament around the acetabulum; The top countries of suppliers are india, china, and india, from. The different bursae of the hip region (trochanteric, ischial and iliopectineal bursae). The depth of the acetabulum and narrowing of its mouth by the acetabular labrum. Hips braces suporter patella stabilizer knee strap brace support for hip. 2, greater sacro sciatic ligament; ► iliofemoral ligament (1 f). The ligament complex on the inside part of the ankle is called the deltoid ligament. Maintain lubrication in the joint by aiding the distribution of synovial fluid. Dislocation of the hip joint. The femur is the upper leg bone or thigh. The iliofemoral ligament, sometimes referred to as the y ligament of bigelow, attaches to the anterior. It's thought that babies in a normal. Additional hip stabilizer in patients with generalized ligamentous laxity, hip dysplasia and in patients with anteroinferior acetabular deficiency. Each hip bone consists of the ilium, ischium, and pubic bone. Distally, it attaches to the intertrochanteric line anteriorly and the femoral neck. Now that we've looked at the articular surfaces of the hip joint, we can now talk about the joint capsule and ligaments. The ligaments of the hip joint are as follows: The firmness of the hip joint is supplied by the following factors which help prevent its dislocation: The pelvis connects the lower extremity to the trunk, protects abdominal and pelvic organs, and provides attachment to muscles and ligaments. Function of the iliofemoral ligament. Kategorie für dateien zu bändern des hüftgelenks. The hip bone, or coxal bone, forms the pelvic girdle portion of the pelvis. Attachments of the ischiofemoral ligament. Ligaments and bones of the hip joint and pelvis. The inguinal ligament supports the muscles that run inferior to its fibers, including the iliopsoas and pectineus muscles of the hip. This is an online quiz called ligaments of the hip.
Hip Joint Bones Movements Muscles Kenhub , The Depth Of The Acetabulum And Narrowing Of Its Mouth By The Acetabular Labrum.
Hip Basicmedical Key. In vertebrate anatomy, hip (or coxa in medical terminology) refers to either an anatomical region or a joint. Inclusive of ischiofemoral ligament, iliofemoral ligament and pubofemoral ligament. Distally, it attaches to the intertrochanteric line anteriorly and the femoral neck. The hip region is located lateral and anterior to the gluteal region, inferior to the iliac crest. Additional hip stabilizer in patients with generalized ligamentous laxity, hip dysplasia and in patients with anteroinferior acetabular deficiency. The firmness of the hip joint is supplied by the following factors which help prevent its dislocation: Dislocation of the hip joint. The main ligaments of the hip and its associated area (iliofemoral, ishciofemoral ligament and pubofemoral ligaments, ligament of bursae of the lower limb: The different bursae of the hip region (trochanteric, ischial and iliopectineal bursae). The ligaments of the hip joint are as follows: Maintain lubrication in the joint by aiding the distribution of synovial fluid. The depth of the acetabulum and narrowing of its mouth by the acetabular labrum. This video identifies all ligaments of the hip. The capsule of the hip joint attaches to the edge of the acetabulum proximally. Aids fine coordination of the hip joint.
Hip Joint . The Support Provided By The Inguinal Ligament Is Important To Maintaining The Flexibility Of The Hip Region While Allowing Vital Blood And Nerve Supply To The Leg.
Slideshow Hip Joint And Pelvic Gateways. This video identifies all ligaments of the hip. The different bursae of the hip region (trochanteric, ischial and iliopectineal bursae). Additional hip stabilizer in patients with generalized ligamentous laxity, hip dysplasia and in patients with anteroinferior acetabular deficiency. Inclusive of ischiofemoral ligament, iliofemoral ligament and pubofemoral ligament. Aids fine coordination of the hip joint. The depth of the acetabulum and narrowing of its mouth by the acetabular labrum. The hip region is located lateral and anterior to the gluteal region, inferior to the iliac crest. The main ligaments of the hip and its associated area (iliofemoral, ishciofemoral ligament and pubofemoral ligaments, ligament of bursae of the lower limb: The firmness of the hip joint is supplied by the following factors which help prevent its dislocation: Distally, it attaches to the intertrochanteric line anteriorly and the femoral neck.
Anatomyexpert Hip Joint And Ligaments Structure Detail , The pelvis connects the lower extremity to the trunk, protects abdominal and pelvic organs, and provides attachment to muscles and ligaments.
Hip Joint Anatomy Hip Bones Ligaments Muscles. Distally, it attaches to the intertrochanteric line anteriorly and the femoral neck. The hip region is located lateral and anterior to the gluteal region, inferior to the iliac crest. This video identifies all ligaments of the hip. Additional hip stabilizer in patients with generalized ligamentous laxity, hip dysplasia and in patients with anteroinferior acetabular deficiency. Maintain lubrication in the joint by aiding the distribution of synovial fluid. Dislocation of the hip joint. The different bursae of the hip region (trochanteric, ischial and iliopectineal bursae). The capsule of the hip joint attaches to the edge of the acetabulum proximally. The depth of the acetabulum and narrowing of its mouth by the acetabular labrum. Aids fine coordination of the hip joint. Inclusive of ischiofemoral ligament, iliofemoral ligament and pubofemoral ligament. The main ligaments of the hip and its associated area (iliofemoral, ishciofemoral ligament and pubofemoral ligaments, ligament of bursae of the lower limb: The ligaments of the hip joint are as follows: The firmness of the hip joint is supplied by the following factors which help prevent its dislocation: In vertebrate anatomy, hip (or coxa in medical terminology) refers to either an anatomical region or a joint.
Ligaments Of The Lumbar Spine And Pelvis : And 2) The Pubofemoral Ligament, Which Checks Hip Abduction And Extension.
Hip Joint. Aids fine coordination of the hip joint. The capsule of the hip joint attaches to the edge of the acetabulum proximally. Additional hip stabilizer in patients with generalized ligamentous laxity, hip dysplasia and in patients with anteroinferior acetabular deficiency. In vertebrate anatomy, hip (or coxa in medical terminology) refers to either an anatomical region or a joint. The ligaments of the hip joint are as follows: The depth of the acetabulum and narrowing of its mouth by the acetabular labrum. This video identifies all ligaments of the hip. The different bursae of the hip region (trochanteric, ischial and iliopectineal bursae). The main ligaments of the hip and its associated area (iliofemoral, ishciofemoral ligament and pubofemoral ligaments, ligament of bursae of the lower limb: Maintain lubrication in the joint by aiding the distribution of synovial fluid. The hip region is located lateral and anterior to the gluteal region, inferior to the iliac crest. Dislocation of the hip joint. Distally, it attaches to the intertrochanteric line anteriorly and the femoral neck. The firmness of the hip joint is supplied by the following factors which help prevent its dislocation: Inclusive of ischiofemoral ligament, iliofemoral ligament and pubofemoral ligament.
Hip Joint Anatomy Hip Bones Ligaments Muscles , In Anatomy, A Ligament Is A Band Or Sheet Of Strong Fibrous Connective Tissue That Connects Bones To Other Bones, Or To Cartilage, Or Supports An Organ, Such As The Spleen, Uterus, Or Eyeball.
Musculoskeletal Pelvic Anatomy Sciencedirect. Aids fine coordination of the hip joint. Additional hip stabilizer in patients with generalized ligamentous laxity, hip dysplasia and in patients with anteroinferior acetabular deficiency. This video identifies all ligaments of the hip. The ligaments of the hip joint are as follows: Distally, it attaches to the intertrochanteric line anteriorly and the femoral neck. The hip region is located lateral and anterior to the gluteal region, inferior to the iliac crest. In vertebrate anatomy, hip (or coxa in medical terminology) refers to either an anatomical region or a joint. Maintain lubrication in the joint by aiding the distribution of synovial fluid. The different bursae of the hip region (trochanteric, ischial and iliopectineal bursae). The main ligaments of the hip and its associated area (iliofemoral, ishciofemoral ligament and pubofemoral ligaments, ligament of bursae of the lower limb: The capsule of the hip joint attaches to the edge of the acetabulum proximally. The depth of the acetabulum and narrowing of its mouth by the acetabular labrum. Dislocation of the hip joint. Inclusive of ischiofemoral ligament, iliofemoral ligament and pubofemoral ligament. The firmness of the hip joint is supplied by the following factors which help prevent its dislocation:
Axis Scientific Life Size Hip Bone Model Premium Hip Joint Model With Flexible Ligaments And Bony Landmarks Includes Base Product Manual And 3 Year Warranty Amazon Com Industrial Scientific : The Hip Bones, Connected By The Pubic Symphysis, And The Vertebrae, Connected By Intervertebral Discs, Are Two Examples Of Symphyses.
Hip Anatomy Physiopedia. The capsule of the hip joint attaches to the edge of the acetabulum proximally. Dislocation of the hip joint. The main ligaments of the hip and its associated area (iliofemoral, ishciofemoral ligament and pubofemoral ligaments, ligament of bursae of the lower limb: Additional hip stabilizer in patients with generalized ligamentous laxity, hip dysplasia and in patients with anteroinferior acetabular deficiency. This video identifies all ligaments of the hip. Aids fine coordination of the hip joint. The hip region is located lateral and anterior to the gluteal region, inferior to the iliac crest. In vertebrate anatomy, hip (or coxa in medical terminology) refers to either an anatomical region or a joint. Maintain lubrication in the joint by aiding the distribution of synovial fluid. Distally, it attaches to the intertrochanteric line anteriorly and the femoral neck. The depth of the acetabulum and narrowing of its mouth by the acetabular labrum. The different bursae of the hip region (trochanteric, ischial and iliopectineal bursae). Inclusive of ischiofemoral ligament, iliofemoral ligament and pubofemoral ligament. The firmness of the hip joint is supplied by the following factors which help prevent its dislocation: The ligaments of the hip joint are as follows:
Cpa 4 2018 Cpa 4 Dpth 6010 Clinical Anatomy Uml Studocu , Media In Category Ligaments Of The Hip.
8 Hip Joint. In vertebrate anatomy, hip (or coxa in medical terminology) refers to either an anatomical region or a joint. Maintain lubrication in the joint by aiding the distribution of synovial fluid. Dislocation of the hip joint. Distally, it attaches to the intertrochanteric line anteriorly and the femoral neck. The hip region is located lateral and anterior to the gluteal region, inferior to the iliac crest. Inclusive of ischiofemoral ligament, iliofemoral ligament and pubofemoral ligament. Additional hip stabilizer in patients with generalized ligamentous laxity, hip dysplasia and in patients with anteroinferior acetabular deficiency. The firmness of the hip joint is supplied by the following factors which help prevent its dislocation: The capsule of the hip joint attaches to the edge of the acetabulum proximally. The depth of the acetabulum and narrowing of its mouth by the acetabular labrum. The main ligaments of the hip and its associated area (iliofemoral, ishciofemoral ligament and pubofemoral ligaments, ligament of bursae of the lower limb: The different bursae of the hip region (trochanteric, ischial and iliopectineal bursae). The ligaments of the hip joint are as follows: This video identifies all ligaments of the hip. Aids fine coordination of the hip joint.
Hip Joint : The Muscles Involved In Hip Motion Are Attached To The Joint At These Trochanters.
The Hip Joint Articulations Movements Teachmeanatomy. The ligaments of the hip joint are as follows: The hip region is located lateral and anterior to the gluteal region, inferior to the iliac crest. Aids fine coordination of the hip joint. Maintain lubrication in the joint by aiding the distribution of synovial fluid. In vertebrate anatomy, hip (or coxa in medical terminology) refers to either an anatomical region or a joint. The main ligaments of the hip and its associated area (iliofemoral, ishciofemoral ligament and pubofemoral ligaments, ligament of bursae of the lower limb: The capsule of the hip joint attaches to the edge of the acetabulum proximally. The different bursae of the hip region (trochanteric, ischial and iliopectineal bursae). The depth of the acetabulum and narrowing of its mouth by the acetabular labrum. The firmness of the hip joint is supplied by the following factors which help prevent its dislocation: Dislocation of the hip joint. Distally, it attaches to the intertrochanteric line anteriorly and the femoral neck. Additional hip stabilizer in patients with generalized ligamentous laxity, hip dysplasia and in patients with anteroinferior acetabular deficiency. Inclusive of ischiofemoral ligament, iliofemoral ligament and pubofemoral ligament. This video identifies all ligaments of the hip.
Hip And Ligaments Flashcards Quizlet : The Sacrospinous Ligament Runs From The Sacrum To The Ischial Spine, And The.
Hip Joint. Dislocation of the hip joint. In vertebrate anatomy, hip (or coxa in medical terminology) refers to either an anatomical region or a joint. The depth of the acetabulum and narrowing of its mouth by the acetabular labrum. The main ligaments of the hip and its associated area (iliofemoral, ishciofemoral ligament and pubofemoral ligaments, ligament of bursae of the lower limb: The firmness of the hip joint is supplied by the following factors which help prevent its dislocation: The hip region is located lateral and anterior to the gluteal region, inferior to the iliac crest. The capsule of the hip joint attaches to the edge of the acetabulum proximally. Distally, it attaches to the intertrochanteric line anteriorly and the femoral neck. Additional hip stabilizer in patients with generalized ligamentous laxity, hip dysplasia and in patients with anteroinferior acetabular deficiency. The ligaments of the hip joint are as follows: Maintain lubrication in the joint by aiding the distribution of synovial fluid. This video identifies all ligaments of the hip. Aids fine coordination of the hip joint. Inclusive of ischiofemoral ligament, iliofemoral ligament and pubofemoral ligament. The different bursae of the hip region (trochanteric, ischial and iliopectineal bursae).
Hip Joint . Now That We've Looked At The Articular Surfaces Of The Hip Joint, We Can Now Talk About The Joint Capsule And Ligaments.
Lateral Hip Pain Side. Maintain lubrication in the joint by aiding the distribution of synovial fluid. This video identifies all ligaments of the hip. Inclusive of ischiofemoral ligament, iliofemoral ligament and pubofemoral ligament. The ligaments of the hip joint are as follows: The depth of the acetabulum and narrowing of its mouth by the acetabular labrum. The hip region is located lateral and anterior to the gluteal region, inferior to the iliac crest. Dislocation of the hip joint. In vertebrate anatomy, hip (or coxa in medical terminology) refers to either an anatomical region or a joint. The firmness of the hip joint is supplied by the following factors which help prevent its dislocation: The different bursae of the hip region (trochanteric, ischial and iliopectineal bursae). Additional hip stabilizer in patients with generalized ligamentous laxity, hip dysplasia and in patients with anteroinferior acetabular deficiency. The capsule of the hip joint attaches to the edge of the acetabulum proximally. Aids fine coordination of the hip joint. The main ligaments of the hip and its associated area (iliofemoral, ishciofemoral ligament and pubofemoral ligaments, ligament of bursae of the lower limb: Distally, it attaches to the intertrochanteric line anteriorly and the femoral neck.